Search engines of all kinds have been a part of our online lives since time immemorial. When the word "search" is mentioned, most of us think of Google. It is considered by many to be an absolute classic in the field, despite the fact that it was not among the first wave of search engines. What were its beginnings?
It could be interest you

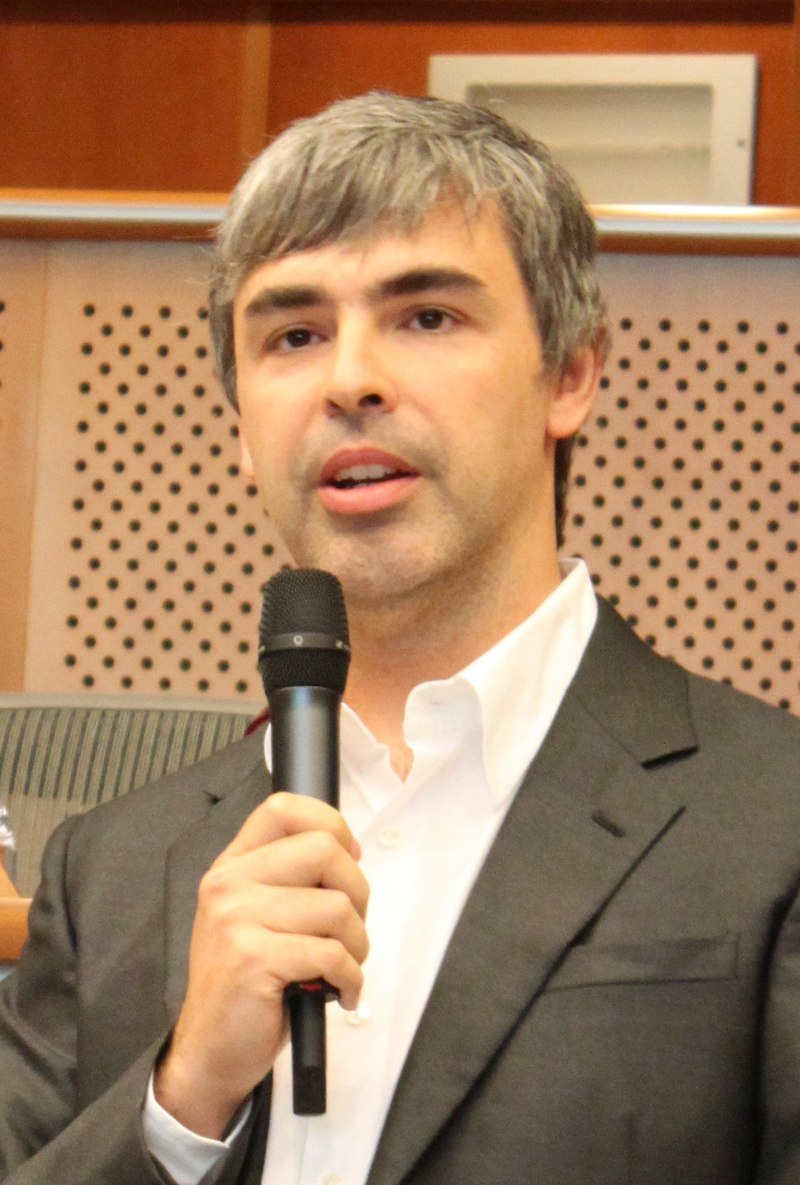
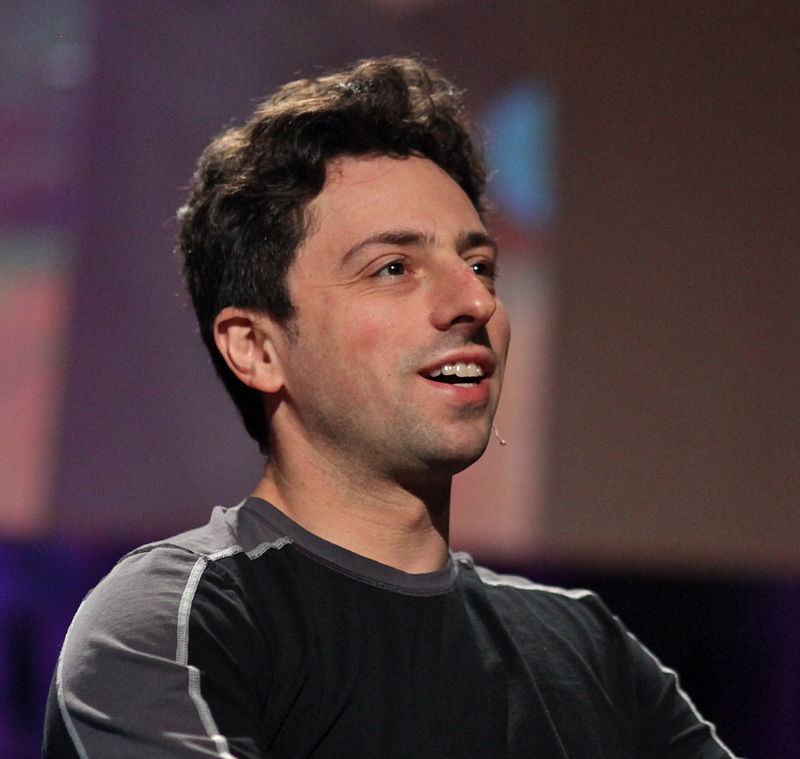
Google as a search engine was invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Its name was inspired by the word "googol", which is an expression that refers to the number 10 to a hundred. According to the founders, the name was supposed to evoke a virtually infinite amount of information that search engines have to sift through. Page and Brin began collaborating in January 1996 on a search program with the working name Backrub. The search engine was unique in that it used a technology developed by Page and Brin called PageRank. It was able to determine the relevance of a given website by taking into account the number of pages or the importance of websites that linked to the respective website. Backrub met with a very positive response, and Page and Brin soon began working on Google development. Their own rooms in college dormitories became their offices, and they created a network server using cheap, used, or borrowed computers. But the attempt to license the fresh search engine was unsuccessful - the pair could not find anyone interested in buying their product at such an early stage of development. So they decided to keep Google, gradually improve it and try to finance it even better.
In the end, the pair managed to fine-tune Google to such an extent that even the co-founder of Sun Microsystems, Andy Bechtolsheim, was enthusiastic about it, who immediately subscribed to the then-nonexistent Google Inc. a check for $100. The registration of Google in the commercial register did not take long, however, as did the help of other investors, including Amazon founder Jeff Bezos. Before long, the founders of Google could afford to rent their first office. It was located in Menlo Park, California. The newly launched beta version of the Google.com browser managed to perform 10 searches every day, and on September 21, 1999, Google officially dropped the "beta" designation. Two years later, Google patented the aforementioned PageRank technology and relocated to larger premises near Palo Alto.
Google's motto was "Do No Evil" - but as its fame and importance grew, so did concerns about whether it could continue to stick to it. In order for the company to continue to live up to its promise to work objectively, without conflict of interests and bias, it established a position for a person whose task was to oversee the observance of the correct company culture. So far, Google has been growing comfortably. During its existence, users gradually received a number of other services and products, such as an online package of web office applications, a custom web browser, a streaming platform, but later also laptops with their own operating system, smartphones, an extensive map and navigation platform, or perhaps a smart speaker.