Almost everything in the world develops over time. As we age, new products, revolutionary technologies and improvements in artificial intelligence are created. Despite the fact that we are gradually moving into the wireless era, we still use cables and video connectors in most cases to transmit images. In this article, let's take a look at the most famous video connectors, or how they have gradually developed over the years.
It could be interest you

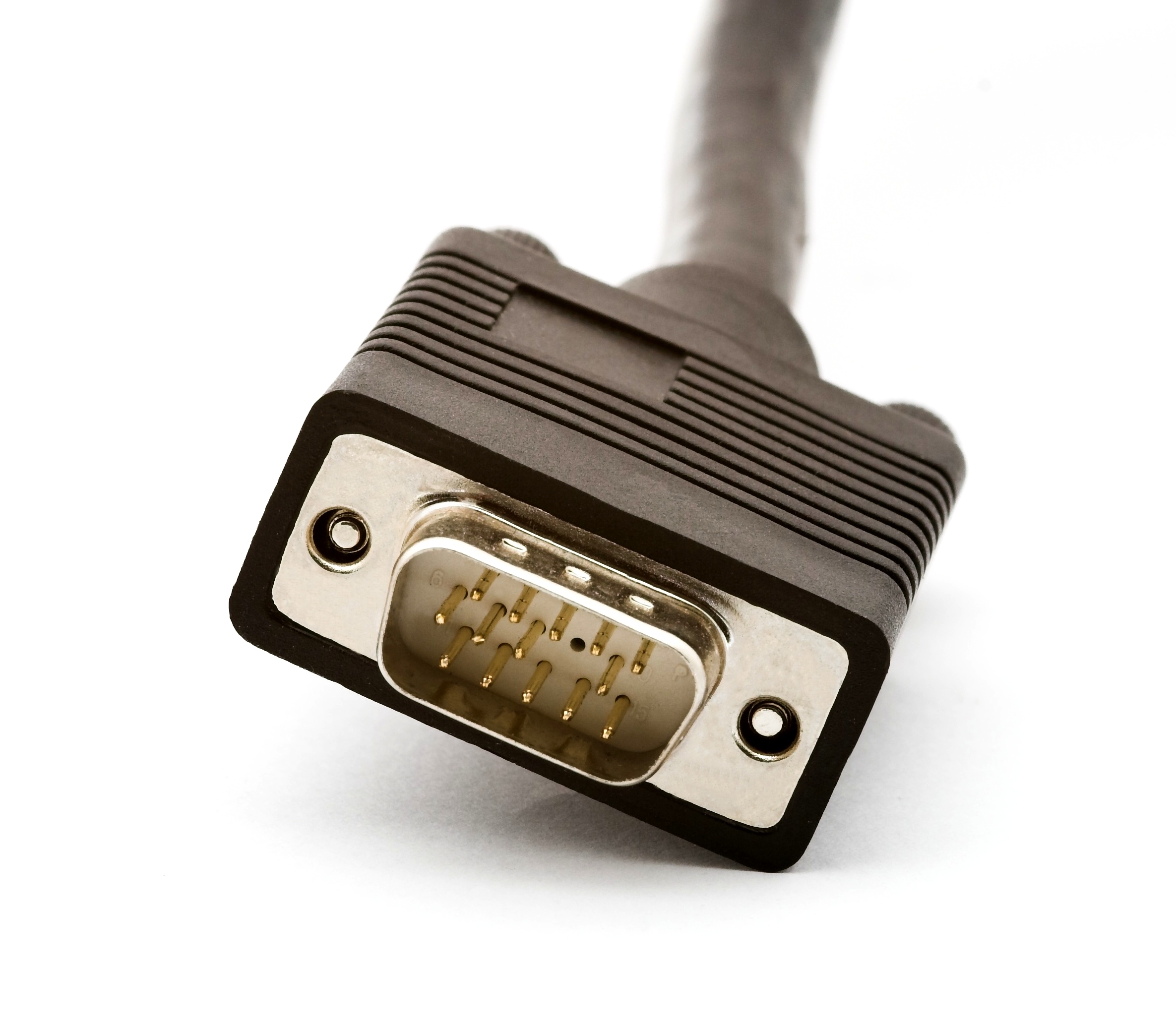
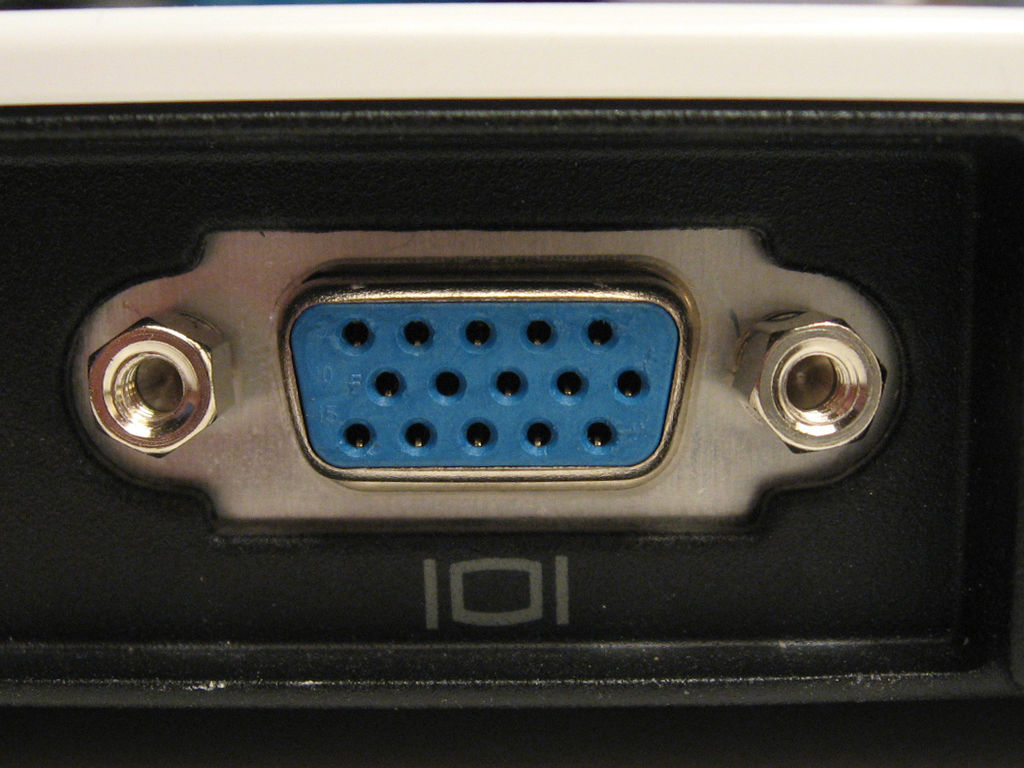
VGA
VGA (Video Graphic Array) is one of the most widespread types of video connectors or cables in the past. You can still find this connector on many devices today, including monitors, televisions and older laptops. IBM is behind this connector, which saw the light of day in 1978. The VGA connector can display a maximum resolution of 640x480 pixels with 16 colors, but if you reduce the resolution to 320x200 pixels, then 256 colors are available - we are talking about the original VGA connector, of course, not its improved versions. The mentioned resolution of 320x200 pixels with 256 colors is the designation for the so-called Mode 13h display, you can encounter it when starting the computer in safe mode, or with some old games. VGA can transmit RGBHV signals, i.e. Red, Blue, Green, Horizontal Sync and Vertical Sync. The cable with the iconic VGA connector often has two screws, thanks to which the cable can be "secured" so that it does not fall out of the connector.
RCA
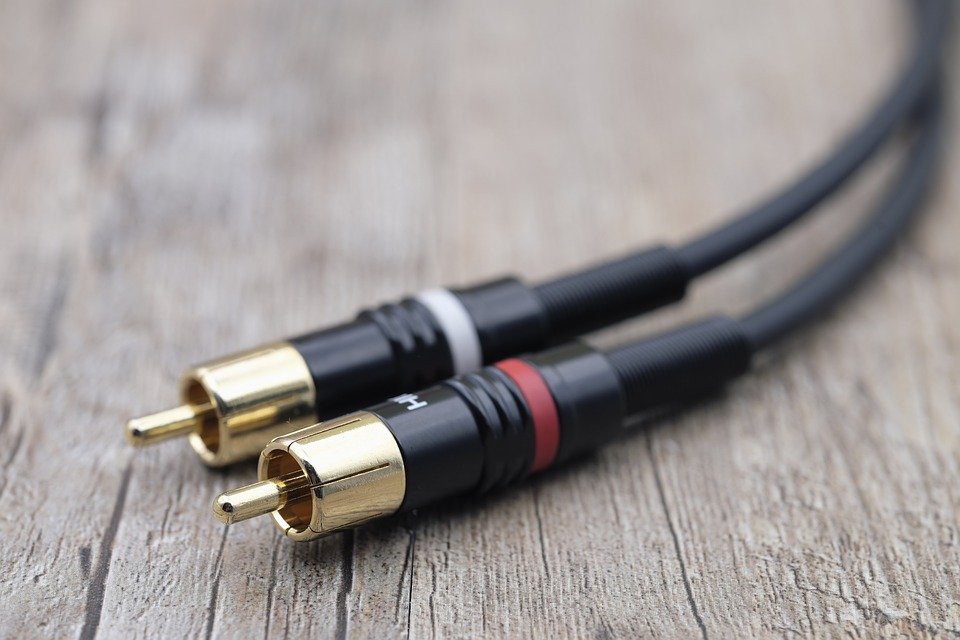
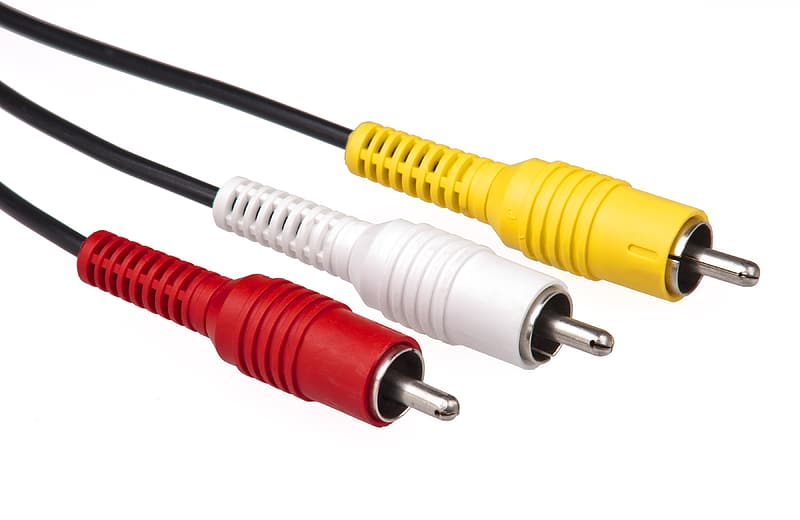
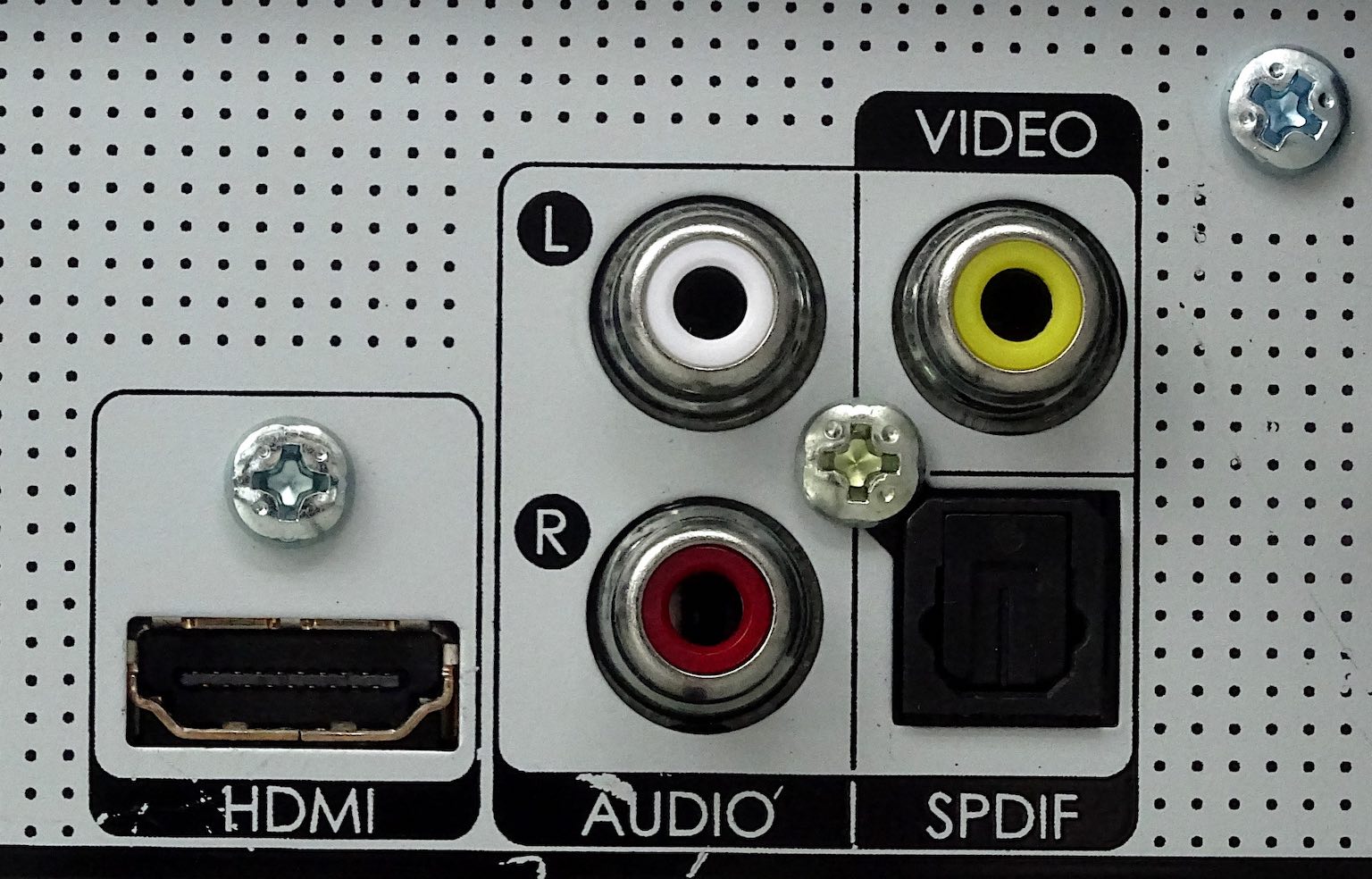
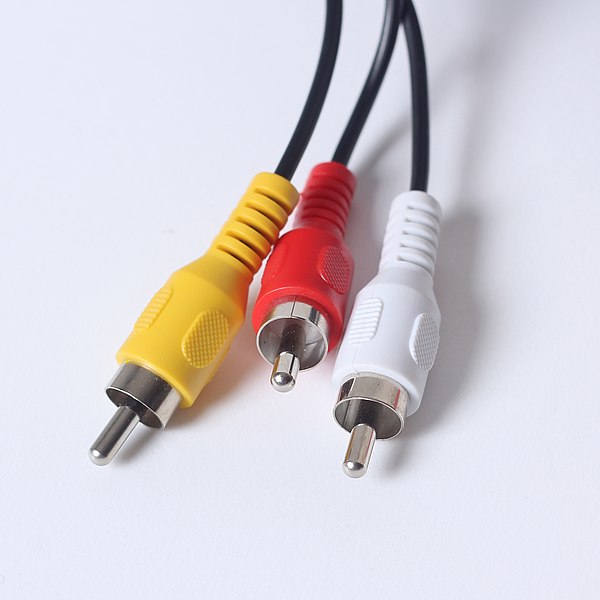
You can distinguish the RCA connector from other video connectors at first glance. This standard uses a total of three cables (special connectors), where one is red, the second white and the third yellow. In addition to video, this connector could also transmit audio, RCA was most often used from the 90s of the last century and at the beginning of the new millennium. At that time, these were completely common and primary connectors for many game consoles (for example, the Nintendo Wii). Many televisions today still support RCA input. The name RCA has nothing to do with the technology itself, it is an abbreviation of the Radio Corporation of America, which popularized this connection. The red and white connector takes care of the audio transmission, the yellow cable then the video transmission. RCA was able to transmit audio with video in 480i or 576i resolution.
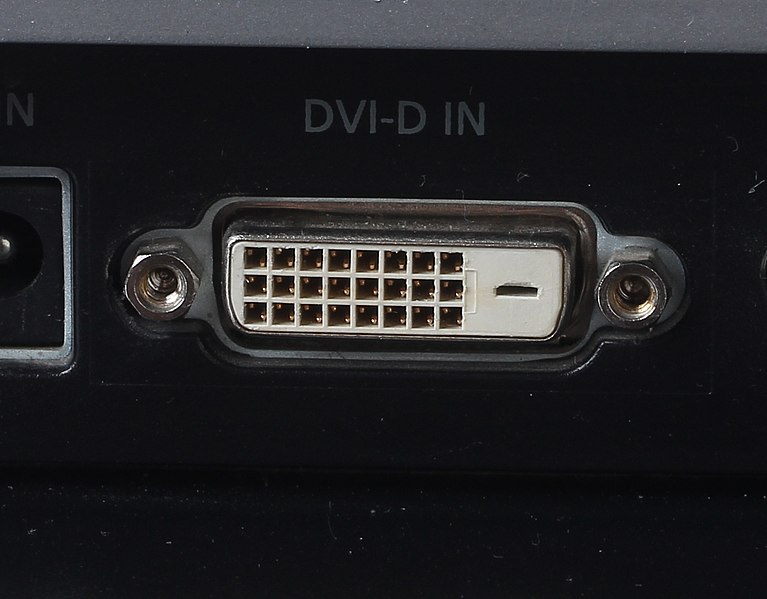
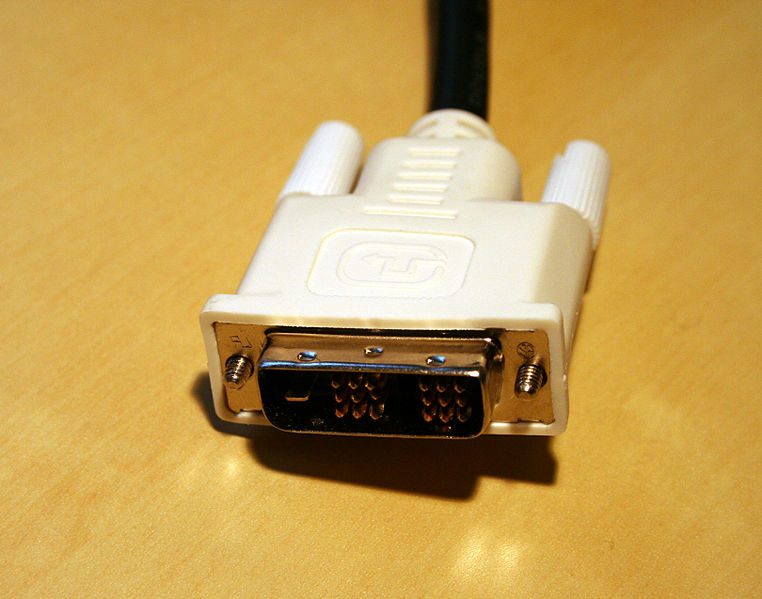
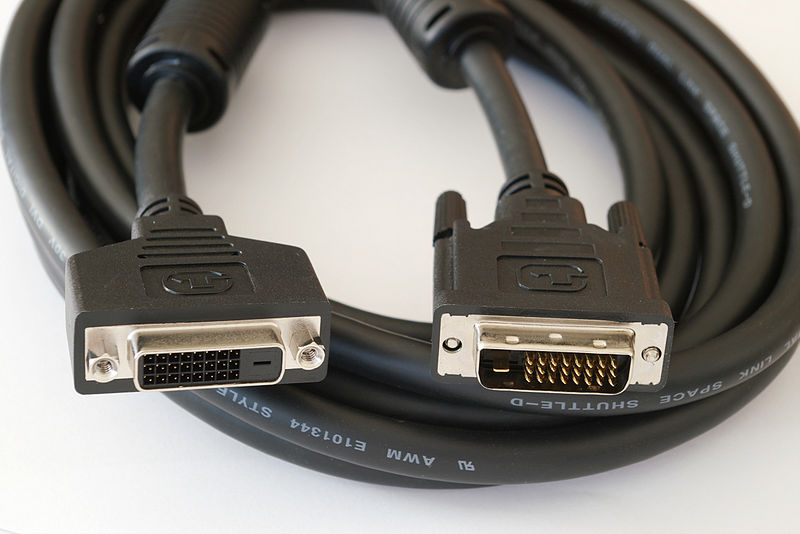
DVI
Digital Visual Interface, abbreviated DVI, saw the light of day in 1999. Specifically, the Digital Display Working group is behind this connector and it is the successor to the VGA connector. The DVI connector can transmit video in three different modes:
- DVI-I (Integrated) combines digital and analog transmission within one connector.
- DVI-D (Digital) only supports digital transmission.
- DVI-A (Analog) supports analog transmission only.
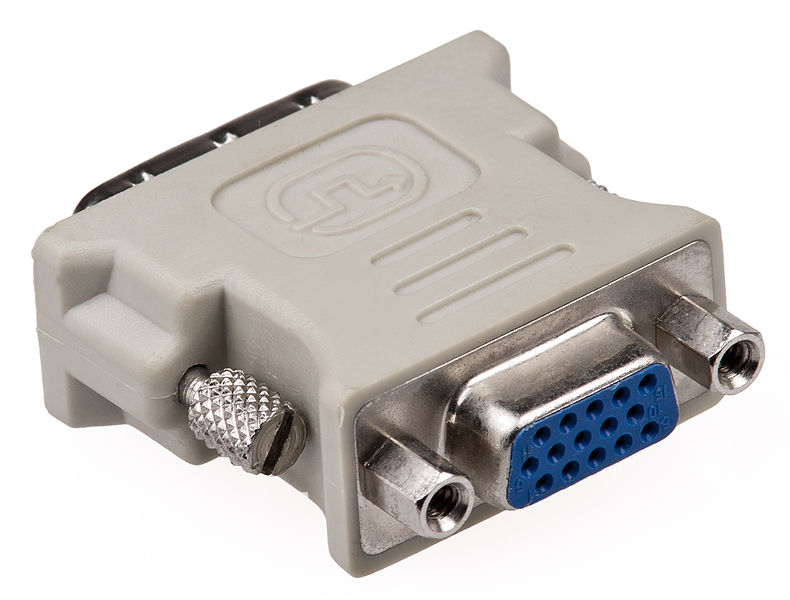
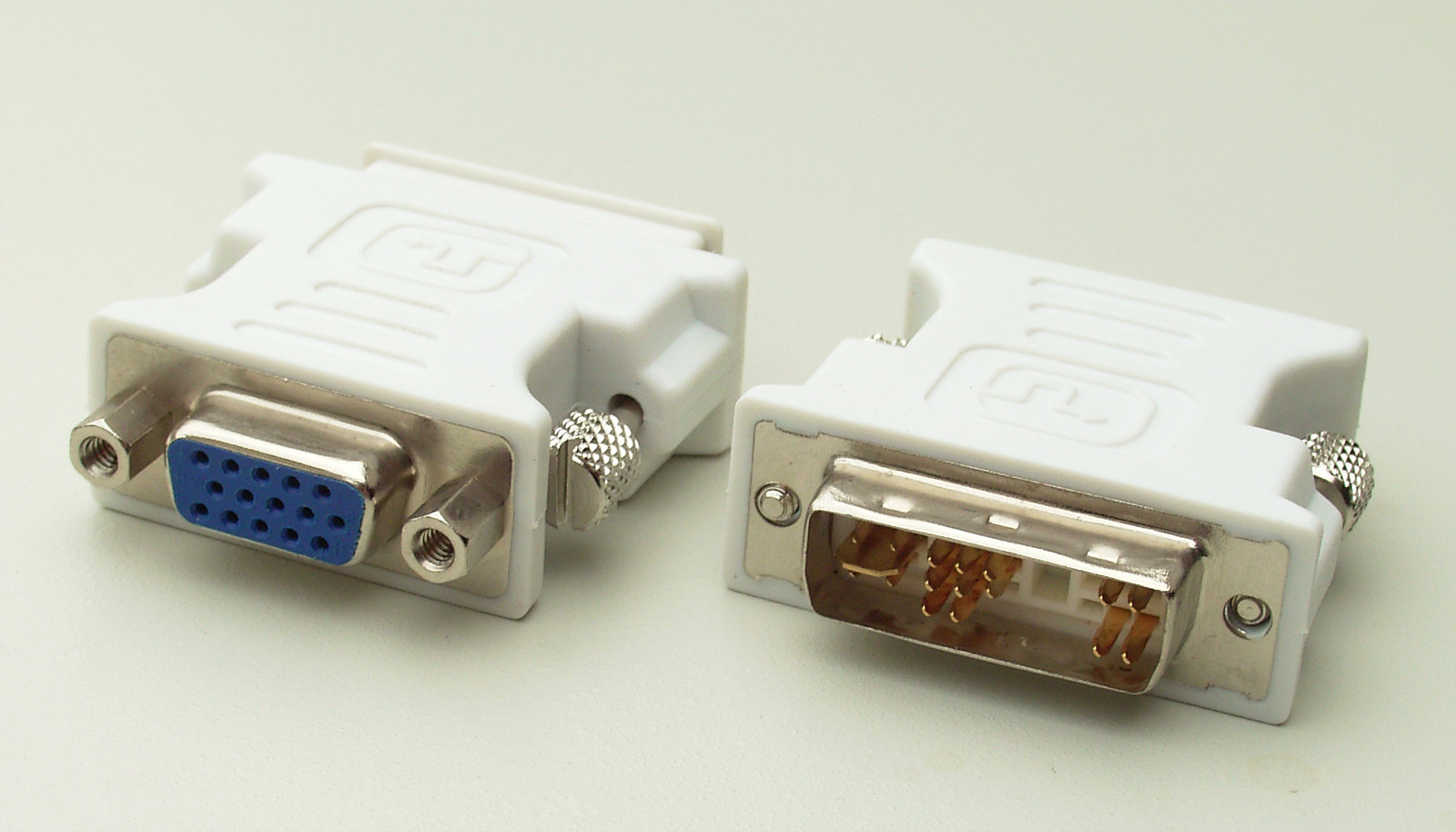
DVI-I and DVI-D were available in single or dual-link variants. The single-link variant was able to transmit video in a resolution of 1920x1200 pixels at a refresh rate of 60 Hz, the dual-link variant then a resolution of up to 2560x1600 pixels at 60 Hz. In order to avoid the very rapid aging of devices with an analog VGA connector, the above-mentioned DVI-A variant was developed, which was able to transmit an analog signal. Thanks to this, you can connect the DVI-A cable to the old VGA using a reducer and everything will work without problems - these reducers are still used today.
HDMI
HDMI - High Definition Media Input - is among the most popular video connectors these days. This interface was developed by combining several companies, namely Sony, Sanyo and Toshiba. HDMI connectors can transmit uncompressed images and audio to computer monitors, external monitors, televisions or even DVD and Blu-ray players. However, the current HDMI is quite different from the first one. The latest version of this connector is the one labeled HDMI 2.1, which saw the light of day three years ago. Thanks to this new version, users could transfer 8K images (from the original 4K resolution), the bandwidth was then increased up to 48 Gbit/s. HDMI cables are backward compatible, so you can use the latest cables even with older devices with an older version of HDMI. The HDMI connector uses the same standards as DVI, which makes these connectors compatible with each other when using a reduction, and in addition, there is no deterioration in image quality. However, unlike HDMI, DVI does not support audio transmission. Three HDMI variants are currently the most common - type A is a classic full-fledged HDMI connector, type C or Mini-HDMI is often used on tablets or laptops, and the smallest Micro-HDMI (type D) can then be found on selected mobile devices.
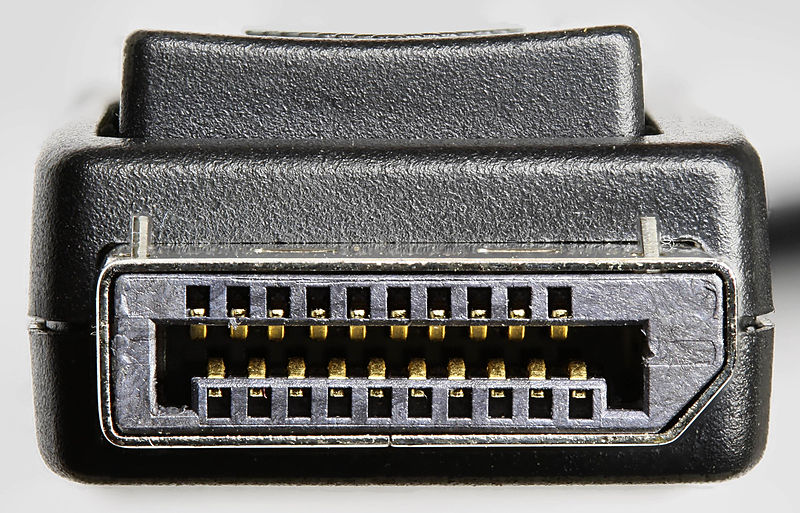
DisplayPort
DisplayPort is a digital interface supported by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is intended for video and audio transmission, in a way it is very similar to the HDMI connector. DisplayPort 2.0 supports the maximum resolution of 8K and HDR, while DisplayPort is often used to connect multiple external monitors for simplicity. However, the HDMI and DisplayPort connectors are intended for different market segments. While HDMI is primarily intended for home "entertainment" devices, DisplayPort is primarily designed to connect computing equipment to monitors. Due to similar properties, DisplayPort and HDMI can be "swapped" in this case as well - just use the Dual-Mode DisplayPort adapter. Using Thunderbolt or Thunderbolt 2 connectors on Macs, you can use mini DisplayPort (for video output) - of course not the other way around (i.e. Mini DisplayPort -> Thunderbolt).
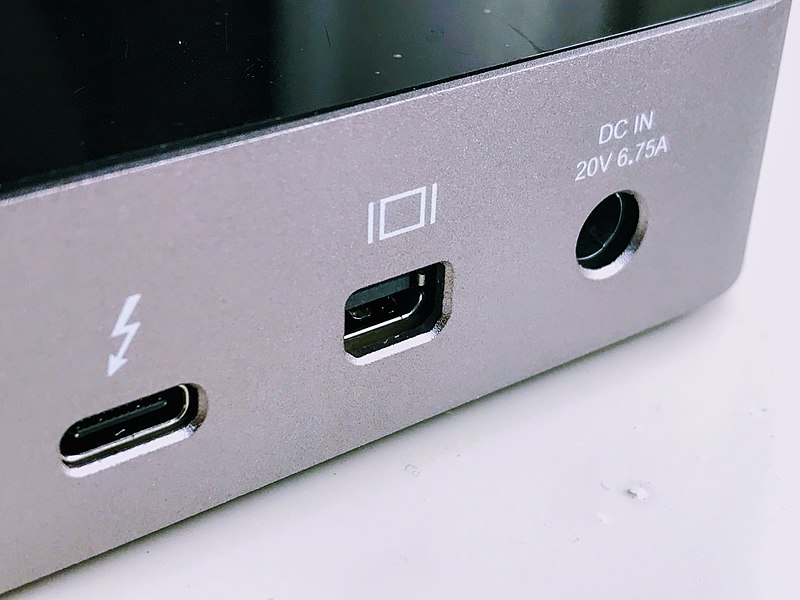
Thunderbolt
The Thunderbolt interface can be found mainly on Apple computers, i.e. for iMacs, MacBooks, etc. Intel collaborated with the apple company on this standard. The first version of this connector had its premiere back in 2011 when the MacBook Pro was introduced. In addition to being able to serve as a video connector, Thunderbolt can do much more. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express and DisplayPort, while also being able to deliver direct current. Thanks to this, you can connect up to 6 different devices using one cable. To make it not so simple, Thunderbolt 3 is compatible with USB-C - however, these standards must not be confused due to their differences. USB-C is weaker and slower than Thunderbolt 3. So if you have Thunderbolt 3 on your device, you can connect a USB-C cable to it with full functionality, but the other way around is not possible.























For God's sake, what kind of amateur knits apples and pears??? The connector is a hardware terminal and the interface is something completely different. E.g. write VGA CONNECTOR has a resolution of 320×200 is a fundamental amateur! The VGA connector supports resolutions from CGA to QXGA. And so on and so forth.
I have a Full HD monitor connected to VGA. So what 640×480. After all, the resolution is determined by the graphics card. The VGA connector is only 15 pins in three rows.
This is a historical issue VGA is a true resolution of 640 x 480
sVGA is 800×600, others have other names, but they are backwards compatible with VGA resolution
And where is the legendary SCART?
On your old TV or on a dusty VCR
Well, not only scart, but also S-Video or BNC connectors.